
The History of Cats
The domestic cat (*Felis catus*) is one of the most popular companions around the world, revered for its independence, playful behavior, and affectionate nature. The journey of the domestic cat, from its wild ancestors to its status as a beloved pet, is a fascinating story that intertwines with human civilization. This essay will explore the history of domestic cats, their domestication, cultural significance, and the evolving relationship they share with humans.
Ancestral Roots

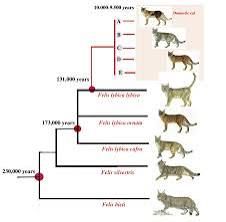
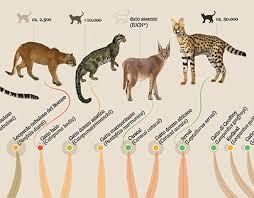
The journey of cats begins with their wild ancestors. The closest relatives of domestic cats are African wildcats (*Felis lybica*), which roamed parts of Africa and the Middle East. Genetic studies suggest that domestic cats diverged from these wild ancestors as early as 9,000 years ago in the Near East, particularly in areas such as modern-day Turkey and the Levant.
As human societies transitioned from nomadic hunter-gatherers to settled agricultural communities during the Neolithic period, the accumulation of grain attracted rodents. This increase in rodent populations drew wildcats to human settlements, creating a mutually beneficial relationship. Wildcats helped control pest populations, while humans provided a steady food source. This form of natural selection led to the domestication of cats, driven not by a conscious effort to domesticate them, but rather through adaptation to human lifestyles.
Development of Domestication
Unlike dogs, which were fully domesticated for tasks such as hunting and herding, cats became semi-domesticated creatures, retaining much of their independence. This relationship was cemented around 4,000 years ago in ancient Egyptian society, where cats began to be revered and bred for their hunting abilities. The Egyptians recognized the value of cats in controlling pests, particularly around grain stores, and they gradually integrated cats into their homes and culture.
Cats were often associated with the goddess Bastet, who represented home, fertility, and domesticity. Egyptian mythology celebrated cats, leading to their mummification upon death and their worship in temples. The high regard for cats in Egypt significantly influenced their spread across the Mediterranean and later into Europe, as sailors and traders took them aboard ships to control infestations.
Cultural Significance

Throughout history, cats have held varied roles in different cultures. In many ancient civilizations, they were praised as symbols of protection and good fortune. For instance, in Norse mythology, the goddess Freyja is often depicted with cats, highlighting their sacred place in society.
In contrast, during the Middle Ages in Europe, cats faced periods of persecution. Misunderstandings and superstition led to the belief that cats were associated with witchcraft. Consequently, many cats were killed, and their populations diminished. However, people’s admiration for cats endured, leading to their resurgence in homes and cities.
As European exploration expanded, cats were transported to new lands, including the Americas. By the 18th and 19th centuries, various breeds began to emerge due to selective breeding practices, helping to establish some of the distinct physical and behavioral traits we recognize today.
Evolution of Breeds

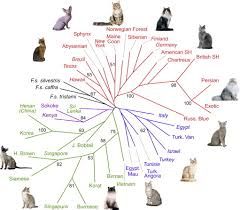
The late 19th and early 20th centuries marked a significant turning point for domestic cats. The establishment of cat shows, beginning in England, encouraged the formal breeding of specific breeds. Breeders aimed to emphasize particular traits, leading to the development of well-known breeds such as the Persian, Siamese, Maine Coon, and British Shorthair. The American Cat Fanciers Association (ACFA) and The International Cat Association (TICA) joined the ranks of breed registries, further codifying the standards and characteristics of various breeds.
Through selective breeding, a wide variety of domestic cat breeds emerged, each with unique physical characteristics and temperaments. This diversity has contributed to the popularity of cats in various households, catering to different preferences and lifestyles.
Cats in Modern Society
Today, domestic cats are valued worldwide as companions and pets. They have adapted to urban living, providing comfort and companionship while embarking on fewer responsibilities compared to dogs. Their independent nature allows them to thrive in smaller living spaces, making them ideal for modern households.
The bond between humans and cats has grown increasingly strong in contemporary society. The rise of the internet has ushered in a new cultural phenomenon—cat memes, videos, and forums dedicated to cat enthusiasts proliferate, celebrating the unique charm and quirks of feline behavior. As pet ownership has increasingly been linked to emotional and psychological benefits, more people have adopted cats, solidifying their status as one of the most popular pets worldwide.
Organizations advocating for strict standards of care, rescue groups, and movement towards spaying and neutering have transformed societal attitudes toward responsible ownership. The importance of adopting cats from shelters rather than purchasing them from breeders has gained popularity, helping to address the issue of feline overpopulation.
Conclusion
The history of domestic cats is a testament to their adaptability and the profoundly intertwined relationship they share with humans. From their wild roots in the African savannah to their revered status in ancient Egypt and their place in modern households, domestic cats continue to captivate our hearts and minds. As we further recognize their intrinsic value as companions, it is essential to continue advocating for their welfare and responsible ownership. The story of the domestic cat reflects not only our appreciation for these enigmatic creatures but also the evolving narrative of companionship, culture, and coexistence in the tapestry of human history.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.